| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Conditions can have several forms, as shown in the following syntax.
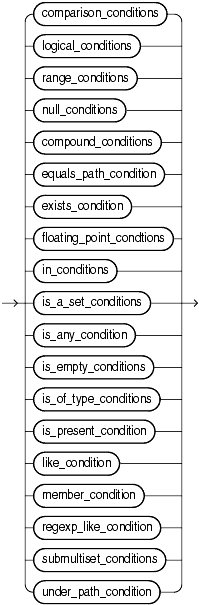
If you have installed Oracle Text, then you can create conditions with the built-in operators that are part of that product, including CONTAINS, CATSEARCH, and MATCHES. For more information on these Oracle Text elements, please refer to Oracle Text Reference.
If you are using Oracle Expression Filter, then you can create conditions with the built-in EVALUATE operator that is part of that product. For more information, please refer to Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Expression Filter.
The sections that follow describe the various forms of conditions. You must use appropriate condition syntax whenever condition appears in SQL statements.
You can use a condition in the WHERE clause of these statements:
DELETE
SELECT
UPDATE
You can use a condition in any of these clauses of the SELECT statement:
WHERE
START WITH
CONNECT BY
HAVING
A condition could be said to be of a logical datatype, although Oracle Database does not formally support such a datatype.
The following simple condition always evaluates to TRUE:
1 = 1
The following more complex condition adds the salary value to the commission_pct value (substituting the value 0 for null) and determines whether the sum is greater than the number constant 25000:
NVL(salary, 0) + NVL(salary + (salary*commission_pct, 0) > 25000)
Logical conditions can combine multiple conditions into a single condition. For example, you can use the AND condition to combine two conditions:
(1 = 1) AND (5 < 7)
Here are some valid conditions:
name = 'SMITH'
employees.department_id = departments.department_id
hire_date > '01-JAN-88'
job_id IN ('SA_MAN', 'SA_REP')
salary BETWEEN 5000 AND 10000
commission_pct IS NULL AND salary = 2100
|
See Also: The description of each statement in Chapter 10 through Chapter 19 for the restrictions on the conditions in that statement |
Precedence is the order in which Oracle Database evaluates different conditions in the same expression. When evaluating an expression containing multiple conditions, Oracle evaluates conditions with higher precedence before evaluating those with lower precedence. Oracle evaluates conditions with equal precedence from left to right within an expression.
Table 6-1 lists the levels of precedence among SQL condition from high to low. Conditions listed on the same line have the same precedence. As the table indicates, Oracle evaluates operators before conditions.
Table 6-1 SQL Condition Precedence
| Type of Condition | Purpose |
|---|---|
| SQL operators are evaluated before SQL conditions | See "Operator Precedence " |
=, !=, <, >, <=, >=, |
comparison |
IS [NOT] NULL, LIKE, [NOT] BETWEEN, [NOT] IN, EXISTS, IS OF type |
comparison |
NOT |
exponentiation, logical negation |
AND |
conjunction |
OR |
disjunction |