| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
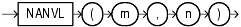
The NANVL function is useful only for floating-point numbers of type BINARY_FLOAT or BINARY_DOUBLE. It instructs Oracle Database to return an alternative value n if the input value m is NaN (not a number). If m is not NaN, then Oracle returns m. This function is useful for mapping NaN values to NULL.
This function takes as arguments any numeric datatype or any nonnumeric datatype that can be implicitly converted to a numeric datatype. Oracle determines the argument with the highest numeric precedence, implicitly converts the remaining arguments to that datatype, and returns that datatype.
|
See Also: Table 2-11, "Implicit Type Conversion Matrix" for more information on implicit conversion, "Floating-Point Numbers " for information on binary-float comparison semantics, and "Numeric Precedence " for information on numeric precedence |
Using table float_point_demo created for TO_BINARY_DOUBLE , insert a second entry into the table:
Insert INTO float_point_demo
VALUES (0,'NaN','NaN');
SELECT * FROM float_point_demo;
DEC_NUM BIN_DOUBLE BIN_FLOAT
---------- ---------- ----------
1234.56 1.235E+003 1.235E+003
0 Nan Nan
The following example returns bin_float if it is not a number. Otherwise, 0 is returned.
SELECT bin_float, NANVL(bin_float,0)
FROM float_point_demo;
BIN_FLOAT NANVL(BIN_FLOAT,0)
---------- ------------------
1.235E+003 1.235E+003
Nan 0