| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
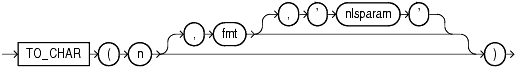
TO_CHAR (number) converts n to a value of VARCHAR2 datatype, using the optional number format fmt. The value n can be of type NUMBER, BINARY_FLOAT, or BINARY_DOUBLE. If you omit fmt, then n is converted to a VARCHAR2 value exactly long enough to hold its significant digits.
Please refer to "Format Models " for information on number formats.
The 'nlsparam' argument specifies these characters that are returned by number format elements:
Decimal character
Group separator
Local currency symbol
International currency symbol
This argument can have this form:
'NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS = ''dg'' NLS_CURRENCY = ''text'' NLS_ISO_CURRENCY = territory '
The characters d and g represent the decimal character and group separator, respectively. They must be different single-byte characters. Within the quoted string, you must use two single quotation marks around the parameter values. Ten characters are available for the currency symbol.
If you omit 'nlsparam' or any one of the parameters, then this function uses the default parameter values for your session.
The following statement uses implicit conversion to combine a string and a number into a number:
SELECT TO_CHAR('01110' + 1) FROM dual;
TO_C
----
1111
Compare this example with the first example for TO_CHAR (character) .
In the next example, the output is blank padded to the left of the currency symbol.
SELECT TO_CHAR(-10000,'L99G999D99MI') "Amount"
FROM DUAL;
Amount
--------------
$10,000.00-
SELECT TO_CHAR(-10000,'L99G999D99MI',
'NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS = '',.''
NLS_CURRENCY = ''AusDollars'' ') "Amount"
FROM DUAL;
Amount
-------------------
AusDollars10.000,00-
In the optional number format fmt, L designates local currency symbol and MI designates a trailing minus sign. See Table 2-14, "Number Format Elements" for a complete listing of number format elements.