| SQL*Plus® User's Guide and Reference Release 10.1 Part Number B12170-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| SQL*Plus® User's Guide and Reference Release 10.1 Part Number B12170-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter explains how to configure your SQL*Plus command-line, Windows GUI, and iSQL*Plus environments. It has the following topics:
These environment variables specify the location or path of files used by SQL*Plus and the iSQL*Plus Application Server. For other environment variables that influence the behavior of SQL*Plus, see the Oracle Database Administrator's Reference.
Table 3-1 Parameters or Environment Variables influencing SQL*Plus and iSQL*Plus
| Parameter or Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| LD_LIBRARY_PATH | Environment variable to specify the path used to search for libraries on UNIX. The environment variable may have a different name on some operating systems, such as LIBPATH, SHLIB_PATH, LD_LIBRARY_PATH64.
Not applicable to Windows Example $ORACLE_HOME/lib |
| LOCAL | Windows environment variable to specify a connection string. Performs the same function as TWO_TASK on UNIX. |
| NLS_LANG | Environment variable to specify globalization behavior.
Example american_america.utf8 |
| ORACLE_HOME | Environment variable to specify where SQL*Plus is installed. It is also used by SQL*Plus to specify where message files are located.
Examples: d:\oracle\10g /u01/app/oracle/product/v10g |
| ORA_NLS10 | Environment variable to specify the locations of the NLS data and the user boot file in SQL*Plus 10.1. The default location is $ORACLE_HOME/nls/data. In a system with both Oracle9i and 10g, or a system under version upgrade, you should set ORA_NLS10 for Oracle 10g and set ORA_NLS33 for 9i. The default NLS location in 9i was $ORACLE_HOME/common/nls/admin/data. |
| ORACLE_PATH | Environment variable to specify the location of SQL scripts. If SQL*Plus cannot find the file in ORACLE_PATH, or if ORACLE_PATH is not set, it searches for the file in the current working directory.
Not applicable to Windows |
| ORACLE_SID | Environment variable to specify the database instance, optional |
| PATH | Environment variable to specify the path to search for executables, and DLLs in Windows. Typically includes ORACLE_HOME/bin |
| SQLPATH | Environment variable or Windows registry entry to specify the location of SQL scripts. SQL*Plus searches for SQL scripts, including login.sql, in the current directory and then in the directories specified by SQLPATH. SQLPATH is a colon separated list of directories. There is no default value set in UNIX installations.
In Windows, SQLPATH is defined in a registry entry during installation. For more information about the SQLPATH registry entry, see "SQLPATH Registry Entry". |
| SQLPLUS | Environment variable to specify the location of SQL*Plus message files in Windows. This environment variable is set during installation. It has a default value of:
%ORACLE_HOME%\SQLPLUS\MESG Not applicable to UNIX. |
| SQLPLUS_FONT | Windows registry entry to specify the font face used in the SQL*Plus Windows GUI. If the SQLPLUS_FONT entry is not created, or if it has an invalid name or value, the default face, Fixedsys, is used. |
| SQLPLUS_FONT_SIZE | Windows registry entry to specify the font size used in the SQL*Plus Windows GUI. If the SQLPLUS_FONT_SIZE entry is not created, or if it has an invalid name or value, the default size, 16, is used. |
| TNS_ADMIN | Environment variable to specify the location of the tnsnames.ora file. If not specified, $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin is used
Example h:\network /var/opt/oracle |
| TWO_TASK | UNIX environment variable to specify a connection string. Connections that do not specify a database will connect to the database specified in TWO_TASK.
Example TWO_TASK=MYDBexport TWO_TASKsqlplus hr/your_password is the same as: sqlplus hr/your_password@MYDB |
| iSQLPlusAllowUserMarkup | iSQL*Plus configuration file option to specify whether HTML, entity mapping replaces characters of special significance with printable representations of those characters. Entity mapping is enabled by default, preventing the use of user defined HTML in iSQL*Plus output. The iSQLPlusAllowUserMarkup option controls whether an iSQL*Plus Application Server enables users to change the entity mapping setting, or use the custom HTML header, body and table tags.
For more information about user defined HTML, see "Enabling User Defined HTML Markup". |
| iSQLPlusConnectIdList | iSQL*Plus configuration file option to specify the databases that users can access in iSQL*Plus. When enabled, a dropdown list of available databases is displayed in place of the Connection Identifier text field on the Login screen. This enables greater security for iSQL*Plus Servers in hosted environments.
For more information about restricted database access, see "Enabling or Disabling Restricted Database Access". |
log4j.rootLogger |
iSQL*Plus configuration file option to specify the level to which messages are logged in the iSQL*Plus Application Server error logs.
For more information about iSQL*Plus logging, see "Setting the Level of iSQL*Plus Logging". |
You can set up your SQL*Plus or iSQL*Plus Application Server environment to use the same settings with each session.
There are two operating system files to do this:
The Site Profile file, glogin.sql, for site wide settings, and settings for the iSQL*Plus sessions from an iSQL*Plus Application Server.
Additionally, in the command-line user interface and the Windows GUI, the User Profile, login.sql, sets user specific settings.
The exact names of these files is system dependent.
The following tables show the profile scripts, and some commands and settings that affect the Command-line, Windows and iSQL*Plus user interfaces.
Table 3-2 Profile Scripts affecting SQL*Plus User Interface Settings
| This script ... |
is run in the Command-line and Windows GUI... | is run in the iSQL*Plus Server ... |
|---|---|---|
| Site Profile (glogin.sql)
Can contain any content that can be included in a SQL*Plus script, such as system variable settings or other global settings the DBA wants to implement. |
After successful Oracle Database connection from a SQLPLUS or CONNECT command.
Where /NOLOG is specified. |
On successful Oracle Database connection from an iSQL*Plus session or a CONNECT command from an iSQL*Plus session. |
| User Profile (login.sql)
Can contain any content that can be included in a SQL*Plus script, but the settings are only applicable to the user's sessions. |
Immediately after the Site Profile. | Not Applicable |
Table 3-3 Commands in Profile scripts affecting SQL*Plus User Interface Settings
| In a profile script, this command ... | affects the Command-line and Windows GUI by ... | affects the iSQL*Plus Server by ... |
|---|---|---|
| SET SQLPLUSCOMPAT[IBILITY] {x.y[.z]}
Also see the "SQL*Plus Compatibility Matrix". |
Setting the SQL*Plus compatibility mode to obtain the behavior the DBA wants for this site. | Setting the SQL*Plus compatibility mode to obtain the behavior the DBA wants for this site. |
| SQLPLUS command COMPATIBILITY Option | As for SET SQLPLUSCOMPATIBILITY but set with the SQLPLUS command COMPATIBILITY option. | Not Applicable |
| SQLPLUS command RESTRICT Option | Starting SQL*Plus with the RESTRICT option set to 3 prevents the User Profile script from being read. | Not Applicable |
A Site Profile script is created during installation. It is used by the database administrator to configure session wide behavior for SQL*Plus Command-line, Windows GUI and iSQL*Plus connections.
The Site Profile script is generally named glogin.sql. SQL*Plus or the iSQL*Plus Server executes this script whenever a user starts a SQL*Plus or iSQL*Plus session and successfully establishes the Oracle Database connection.
The Site Profile enables the DBA to set up SQL*Plus environment defaults for all users of a particular SQL*Plus or iSQL*Plus Application Server installation
Users cannot directly access the Site Profile.
The Site Profile script is $ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/glogin.sql in UNIX, and %ORACLE_HOME%\sqlplus\admin\glogin.sql in Windows. If a Site Profile already exists at this location, it is overwritten when you install SQL*Plus. If SQL*Plus is removed, the Site Profile script is deleted.
The default Site Profile script contains the following:
-- -- Copyright (c) 1988, 2003, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. -- -- NAME -- glogin.sql -- -- DESCRIPTION -- SQL*Plus global login "site profile" file -- -- Add any SQL*Plus commands here that are to be executed when a -- user starts SQL*Plus, or uses the SQL*Plus CONNECT command -- -- USAGE -- This script is automatically run -- -- Used by Trusted Oracle COLUMN ROWLABEL FORMAT A15 -- Used for the SHOW ERRORS command COLUMN LINE/COL FORMAT A8 COLUMN ERROR FORMAT A65 WORD_WRAPPED -- Used for the SHOW SGA command COLUMN name_col_plus_show_sga FORMAT a24 -- Defaults for SHOW PARAMETERS COLUMN name_col_plus_show_param FORMAT a36 HEADING NAME COLUMN value_col_plus_show_param FORMAT a30 HEADING VALUE -- Defaults for SHOW RECYCLEBIN COLUMN origname_plus_show_recyc FORMAT a16 HEADING 'ORIGINAL NAME' COLUMN objectname_plus_show_recyc FORMAT a30 HEADING 'RECYCLEBIN NAME' COLUMN objtype_plus_show_recyc FORMAT a12 HEADING 'OBJECT TYPE' COLUMN droptime_plus_show_recyc FORMAT a19 HEADING 'DROP TIME' -- Defaults for SET AUTOTRACE EXPLAIN report COLUMN id_plus_exp FORMAT 990 HEADING i COLUMN parent_id_plus_exp FORMAT 990 HEADING p COLUMN plan_plus_exp FORMAT a60 COLUMN object_node_plus_exp FORMAT a8 COLUMN other_tag_plus_exp FORMAT a29 COLUMN other_plus_exp FORMAT a44
For SQL*Plus command-line and Windows GUI connections, SQL*Plus also supports a User Profile script. The User Profile is executed after the Site Profile and is intended to allow users to specifically customize their session. The User Profile script is generally named login.sql. SQL*Plus searches for the User Profile in your current directory, and then the directories you specify with the SQLPATH environment variable. SQL*Plus searches this colon-separated list of directories in the order they are listed.
You can add any SQL commands, PL/SQL blocks, or SQL*Plus commands to your user profile. When you start SQL*Plus, it automatically searches for your user profile and runs the commands it contains.
A user profile is not used in iSQL*Plus.
You can modify your LOGIN file just as you would any other script. The following sample User Profile script shows some modifications that you could include:
-- login.sql -- SQL*Plus user login startup file. -- -- This script is automatically run after glogin.sql -- -- To change the SQL*Plus prompt to display the current user, -- connection identifier and current time. -- First set the database date format to show the time. ALTER SESSION SET nls_date_format = 'HH:MI:SS'; -- SET the SQLPROMPT to include the _USER, _CONNECT_IDENTIFIER -- and _DATE variables. SET SQLPROMPT "_USER'@'_CONNECT_IDENTIFIER _DATE> " -- To set the number of lines to display in a report page to 24. SET PAGESIZE 24 -- To set the number of characters to display on each report line to 78. SET LINESIZE 78 -- To set the number format used in a report to $99,999. SET NUMFORMAT $99,999
|
See Also:
|
From the Command-line and Windows GUI you can store the current SQL*Plus system variables in a script with the STORE command. If you alter any variables, this script can be run to restore the original values. This is useful if you want to reset system variables after running a report that alters them. You could also include the script in your User Profile script so that these system variables are set each time you start SQL*Plus.
To store the current setting of all system variables, enter
STORE SET file_name
Enter a file name and file extension, or enter only the file name to use the default extension "SQL". You can use the SET SUFFIX command to change the default file extension.
To restore the stored system variables, enter
START file_name
If the file has the default extension (as specified by the SET SUFFIX command), you do not need to add the period and extension to the file name.
You can also use the @ ("at" sign) or the @@ (double "at" sign) commands to run the script.
Example 3-1 Storing and Restoring SQL*Plus System Variables
To store the current values of the SQL*Plus system variables in a new script "plusenv.sql":
STORE SET plusenv
Created file plusenv |
Now the value of any system variable can be changed:
SHOW PAGESIZE
PAGESIZE 24 |
SET PAGESIZE 60 SHOW PAGESIZE
PAGESIZE 60 |
The original values of system variables can then be restored from the script:
START plusenv SHOW PAGESIZE
PAGESIZE 24 |
In Windows, use the batch file, HELPINS.BAT, available in
%ORACLE_HOME%\BIN
In UNIX, set an environment variable, SYSTEM_PASS, to hold the SYSTEM user login with:
SYSTEM_PASS=SYSTEM/password EXPORT SYSTEM_PASS
In Windows, set SYSTEM_PASS with:
SET SYSTEM_PASS=SYSTEM/password
where password is the password you have defined for the SYSTEM user.
In UNIX, run the shell script, HELPINS, from a terminal with:
$ORACLE_HOME/BIN/HELPINS
In Windows, run the batch file, HELPINS.BAT, from the command-line with:
%ORACLE_HOME%\BIN\HELPINS
In either case, the HELPINS utility reads the login from SYSTEM_PASS to connect to Oracle Database using SQL*Plus, creates and loads the help tables, and then disconnects. You can use command-line help the next time you start SQL*Plus.
Run the provided SQL script, HLPBLD.SQL, to load command-line help.
Log in to SQL*Plus as the SYSTEM user with:
SQLPLUS SYSTEM/your_password
where your_password is the password you have defined for the SYSTEM user.
In UNIX run the SQL script, HLPBLD.SQL, from SQL*Plus with:
@$ORACLE_HOME/SQLPLUS/ADMIN/HELP/HLPBLD.SQL HELPUS.SQL
In Windows run the SQL script, HLPBLD.SQL, from SQL*Plus with:
@%ORACLE_HOME%\SQLPLUS\ADMIN\HELP\HLPBLD.SQL HELPUS.SQL
The HLPBLD.SQL script creates and loads the help tables.
Run the provided SQL script, HELPDROP.SQL, to remove the command-line help.
Log in to SQL*Plus as the SYSTEM user with:
SQLPLUS SYSTEM/your_password
where your_password is the password you have defined for the SYSTEM user.
In UNIX run the SQL script, HELPDROP.SQL, from SQL*Plus with:
@$ORACLE_HOME/SQLPLUS/ADMIN/HELP/HELPDROP.SQL
In Windows run the SQL script, HELPDROP.SQL, from SQL*Plus with:
@%ORACLE_HOME%\SQLPLUS\ADMIN\HELP\HELPDROP.SQL
The HELPDROP.SQL script drops the help tables, and then disconnects.
If you plan to connect to a database other than the default, whether on the same computer or another computer, you need to ensure that Oracle Net is installed, and the database listener is configured and running. Oracle Net services are used by SQL*Plus and the iSQL*Plus Application Server.
Oracle Net services and the database listener are installed by default during Oracle Database installation. For further information about installing and configuring Oracle Net, see the Oracle Database documentation at http://otn.oracle.com/documentation.
You can set the following behavior and security settings on the iSQL*Plus Application Server:
After Oracle Database installation, if you are unable to connect to your iSQL*Plus Server, check that your Application Server is running, and that you are using the correct URL to connect to it. If you are still unable to connect, it may be because the port that the Application Server is attempting to use is already in use by another application. There is no consistent message to indicate that the port is already in use. A message, if any, depends on the application using the port.
Open the configuration file, http-web-site.xml, located in
$ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/isqlplus/config
Search for the web-site element. It has the form
<website port="5560" display-name="Oracle9iAS Containers for J2EE HTTP Web Site">
The value specified by the attribute, port, is the port number that the Application Server is attempting to use.
To view currently used ports and determine if the Application Server is trying to use a port that is already in use, run the following command:
netstat -an
If there is another application using the same port, you need to change the port used by the Application Server to a number that is not in use. By convention, it is recommended that you use a port number above 2000, and that you do not use 80 or 8080 as they are usually used by web services. A port number can be any unique integer number.
Stop the Application Server.
Open the configuration file, http-web-site.xml, located in
$ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/isqlplus/config
Search for the web-site element. It has the form
<website port="5560" display-name="Oracle9iAS Containers for J2EE HTTP Web Site">
The number specified by the attribute, port, is the port number that the Application Server is attempting to use.
Change the port number to a unique port number that you want the iSQL*Plus Application Server to use.
Save http-web-site.xml.
Restart the iSQL*Plus Application Server.
You can use operating system utilities to determine if the iSQL*Plus Application Server is running. On Windows, the iSQL*Plus Application Server can be run as a Windows Service, or can be started from a Windows command prompt.
Open a terminal.
Enter the following command to find the iSQL*Plus Application Server process:
$ ps -eaf|grep Djava
One of the lines returned should be something like:
oracle 6082 1 0 Nov 05 pts/8 28:42 $ORACLE_HOME/jdk/bin/java -Djava.awt.headless=true -Djava.security.properties=/
This running process is the iSQL*Plus Application Server.
Select Services from the Start > Programs > Administrative Tools menu.
Find the iSQL*Plus Windows service, called OracleOracleHomeNameiSQL*Plus.
Check the status of the Windows service to see whether it is started.
iSQL*Plus can also be started from a Windows command prompt. To determine whether the iSQL*Plus Application Server was started and is running from the command line, check whether there is an open Windows command prompt containing messages similar to:
C:\isqlplusctl start iSQL*Plus 10.1.0.2.0 Copyright (c) 2003 Oracle. All rights reserved. Starting iSQL*Plus ... iSQL*Plus started.
The log4j.rootLogger parameter determines whether logging of iSQL*Plus Application Server messages is enabled. It also sets the level to which messages are logged in the iSQL*Plus Application Server error logs. There should be no need to change its value unless instructed to do so by Oracle Support. Logging is useful to help resolve user problems.
The log4j.rootLogger parameter is in the log4j.properties file, located in the directory:
$ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/oc4j_applications/applications/isqlplus/isqlplus/WEB-INF
Logging can be set to ALL errors and messages, DEBUG messages, INFO messages, WARNing messages, ERROR messages, FATAL errors, or to OFF. The settings are changed by commenting or uncommenting the required lines in the log4j.properties file. The following example shows the default setting, which is to log FATAL errors:
# Set root logger level and its only appender to A1. #log4j.rootLogger=ALL, A1 #log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, A1 #log4j.rootLogger=INFO, A1 #log4j.rootLogger=WARN, A1 #log4j.rootLogger=ERROR, A1 log4j.rootLogger=FATAL, A1 #log4j.rootLogger=OFF, A1
The iSQL*Plus log file is written to:
$ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/isqlplus/application-deployments/isqlplus/application.log
The iSQL*Plus Help log file is written to:
$ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/isqlplus/application-deployments/isqlplushelp/application.log
Timing out iSQL*Plus sessions helps to reduce machine load and to maximize resources. The time out interval is set by the session-timeout element. It defines the time a session can be idle before it is expired.
You can edit the web.xml configuration file to change the timeout interval. The web.xml file is located in the directory:
$ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/oc4j_applications/applications/isqlplus/isqlplus/WEB-INF
In the web.xml file, search for the <session-timeout> element inside <session-config>. The syntax of the line to change in the configuration file is:
<session-config> <session-timeout>15</session-timeout> </session-config>
Where the value is the number of whole minutes of idle time before the session times out. It has a default value of 15 minutes. It can be set to any value from 1 to 1440 minutes. It should not be set so small that users do not get a chance to enter their scripts.When a user tries to use a timed out iSQL*Plus session, the Login screen is displayed and the user is prompted to log in again. The following error is displayed: SP2-0864: Session has expired. Please log in again.
You may want to limit the databases that users can access in iSQL*Plus to a restricted list. When restricted database access has been enabled, a dropdown list of available databases is displayed in place of the Connection Identifier text field on the Login screen. This enables greater security for iSQL*Plus Servers in hosted environments. Connection identifiers are listed in the order defined in iSQLPlusConnectIdList.
Edit the $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/oc4j-applications/applications/isqlplus/isqlplus/WEB-INF/web.xml file to restrict database access to iSQL*Plus users. Change the following entry to include a new param-value element which contains the list of databases to which you want to restrict access, for example
<init-param>
<param-name>iSQLPlusConnectIdList</param-name> <description>The database(s) to which iSQL*Plus users are restricted. The list should contain the Oracle SIDs or SERVICE_NAMEs, separated by a semicolon (;). If there are no entries, database access is not restricted through iSQL*Plus.</description> <param-value>ora10g;ora9i</param-value>
</init-param>
Entries in the param-value element should be identical to the alias for SERVICE_NAMEs or SIDs set in your $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora file.
Restart iSQL*Plus for your changes to take effect.
Connection identifiers are case insensitive, and each connection identifier listed in the argument should be identical to an alias in the tnsnames.ora file.
Once set, all connections made through the Login screen, all dynamic reports and any connections attempted with the CONNECT command are refused unless the connection is to one of the databases in the restricted list. Similarly, if SET INSTANCE is used, the connection identifier defined must match an entry in iSQLPlusConnectIdList or the connection is refused.
If no connection identifier is given, or if the one given does not match an entry in iSQLPlusConnectIdList, the database connection is refused and the following error occurs:
SP2-0884: Connection to database database_name is not allowed
To access the iSQL*Plus DBA URL, you must set up the OC4J user manager. You can set up OC4J to use:
The XML-based provider type, jazn-data.xml
The LDAP-based provider type, Oracle Internet Directory
This document discusses how to set up the iSQL*Plus DBA URL to use the XML-based provider. For information on how to set up the LDAP-based provider, see the Oracle9iAS Containers for J2EE documentation.
Create users for the iSQL*Plus DBA URL.
Grant the webDba role to users.
Test iSQL*Plus DBA Access.
The Oracle JAAS Provider, otherwise known as JAZN (Java AuthoriZatioN), is Oracle's implementation of the Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS). Oracle's JAAS Provider is referred to as JAZN in the remainder of this document. See the Oracle9iAS Containers for J2EE documentation for more information about JAZN, the Oracle JAAS Provider.
The actions available to manage users for the iSQL*Plus DBA URL are:
Create users
List users
Grant the webDba role
Remove users
Revoke the webDba role
Change user passwords
You perform these actions from the $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/isqlplus/application-deployments/isqlplus directory.
$JAVA_HOME is the location of your JDK (1.4 or above). It should be set to $ORACLE_HOME/jdk, but you may use another JDK.
admin_password is the password for the iSQL*Plus DBA realm administrator user, admin. The password for the admin user is set to 'welcome' by default. You should change this password as soon as possible. See Change User Passwords.
A JAZN shell option, and a command line option are given for all steps.
To start the JAZN shell, enter:
$JAVA_HOME/bin/java -Djava.security.properties=$ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/iplus/provider -jar $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/home/jazn.jar -user "iSQL*Plus DBA/admin" -password admin_password -shell
To exit the JAZN shell, enter:
EXIT
You can create multiple users who have access to the iSQL*Plus DBA URL. To create a user from the JAZN shell, enter:
JAZN> adduser "iSQL*Plus DBA" username password
To create a user from the command-line, enter:
$JAVA_HOME/bin/java -Djava.security.properties=$ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/iplus/provider -jar $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/home/jazn.jar -user "iSQL*Plus DBA/admin" -password admin_password -adduser "iSQL*Plus DBA" username password
username and password are the username and password used to log into the iSQL*Plus DBA URL.
To create multiple users, repeat the above command for each user.
You can confirm that users have been created and added to the iSQL*Plus DBA realm. To confirm the creation of a user using the JAZN shell, enter:
JAZN> listusers "iSQL*Plus DBA"
To confirm the creation of a user using the command-line, enter:
$JAVA_HOME/bin/java -Djava.security.properties=$ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/iplus/provider -jar $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/home/jazn.jar -user "iSQL*Plus DBA/admin" -password admin_password -listusers "iSQL*Plus DBA"
The usernames you created are displayed.
Each user you created above must be granted access to the webDba role. To grant a user access to the webDba role from the JAZN shell, enter:
JAZN> grantrole webDba "iSQL*Plus DBA" username
To grant a user access to the webDba role from the command-line, enter:
$JAVA_HOME/bin/java -Djava.security.properties=$ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/iplus/provider -jar $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/home/jazn.jar -user "iSQL*Plus DBA/admin" -password admin_password -grantrole webDba "iSQL*Plus DBA" username
To remove a user using the JAZN shell, enter:
JAZN> remuser "iSQL*Plus DBA" username
To remove a user using the command-line, enter:
$JAVA_HOME/bin/java -Djava.security.properties=$ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/iplus/provider -jar $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/home/jazn.jar -user "iSQL*Plus DBA/admin" -password admin_password -remuser "iSQL*Plus DBA" username
To revoke a user's webDba role from the JAZN shell, enter:
JAZN> revokerole webDba "iSQL*Plus DBA" username
To revoke a user's webDba role from the command-line, enter:
$JAVA_HOME/bin/java -Djava.security.properties=$ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/iplus/provider -jar $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/home/jazn.jar -user "iSQL*Plus DBA/admin" -password admin_password -revokerole "iSQL*Plus DBA" username
To change a user's password from the JAZN shell, enter:
JAZN> setpasswd "iSQL*Plus DBA" username old_password new_password
To change a user's password from the command-line, enter:
$JAVA_HOME/bin/java -Djava.security.properties=$ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/iplus/provider -jar $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/home/jazn.jar -user "iSQL*Plus DBA/admin" -password admin_password -setpasswd "iSQL*Plus DBA" username old_password new_password
Test iSQL*Plus DBA access by entering the iSQL*Plus DBA URL in your web browser:
http://machine_name.domain:5560/isqlplus/dba
A dialog is displayed requesting authentication for the iSQL*Plus DBA URL. Log in as the user you created above. You may need to restart iSQL*Plus for the changes to take effect.
This is an example of setting up iSQL*Plus to use SSL. This procedure assumes that you have an existing certificate. If not, you can request a certificate from a certification authority (CA). Many CAs provide test certificates for use during testing.
For this procedure, set $JAVA_HOME to $ORACLE_HOME/jdk, and perform the following steps from the $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee directory.
Use the keytool utility to generate the keypair (public and private keys), and a keystore (database) to store the keypair:
$JAVA_HOME/bin/keytool -genkey -keyalg "RSA" -keystore keystore -storepass 123456 -validity 100
This example uses RSA as the key algorithm, keystore as the storage file name to store the keys, sets the password to access the storage file as 123456, and is valid for 100 days. The keytool utility then prompts you for further information:
What is your first and last name? [Unknown]: Test User What is the name of your organizational unit? [Unknown]: IT Department What is the name of your organization? [Unknown]: Oracle Corporation What is the name of your City or Locality? [Unknown]: San Francisco What is the name of your State or Province? [Unknown]: California What is the two-letter country code for this unit? [Unknown]: US Is CN=Test User, OU=IT Department, O=Oracle Corporation, L=San Francisco, ST=California, C=US correct? =[no]: yes Enter key password for <mykey> (RETURN if same as keystore password):
A storage file named keystore is generated in the current directory.
Load your server's root certificate into the storage file you created in the step 1.
$JAVA_HOME/bin/keytool -keystore keystore -import -alias servertest -file servertest.cer Enter keystore password: 123456 Owner: CN=Thawte Test CA Root, OU=TEST TEST TEST, O=Thawte Certification, ST=FO TESTING PURPOSES ONLY, C=ZA Issuer: CN=Thawte Test CA Root, OU=TEST TEST TEST, O=Thawte Certification, ST=F R TESTING PURPOSES ONLY, C=ZA Serial number: 0 Valid from: Thu Aug 01 10:00:00 EST 1996 until: Fri Jan 01 08:59:59 EST 2021 Certificate fingerprints: MD5: 5E:E0:0E:1D:17:B7:CA:A5:7D:36:D6:02:DF:4D:26:A4 SHA1: 39:C6:9D:27:AF:DC:EB:47:D6:33:36:6A:B2:05:F1:47:A9:B4:DA:EA Trust this certificate? [no]: yes Certificate was added to keystore
In this example, an alias, servertest, is created for the root certificate, servertest.cer.
Create a certificate request to request a certificate from your CA.
$JAVA_HOME/bin/keytool -certreq -keystore keystore -file mycsr.csr Enter keystore password: 123456
In this example, the certificate request file is named mycsr.csr. Use the contents of mycsr.csr to request a new certificate from your CA. Create a new file called mycert.cer and paste in the contents of your new certificate.
Import the new certificate obtained in the previous step into the storage file.
$JAVA_HOME/bin/keytool -import -trustcacerts -file mycert.cer Enter keystore password: 123456 Owner: CN=Test User, OU=IT Department, O=Oracle Corporation, L=San Francisco, ST=California, C=US Issuer: CN=Thawte Test CA Root, OU=TEST TEST TEST, O=Thawte Certification, ST=FOR TESTING PURPOSES ONLY, C=ZA Serial number: 7988 Valid from: Thu Sep 04 14:12:45 EST 2003 until: Thu Sep 25 14:12:45 EST 2003 Certificate fingerprints: MD5: F3:E2:1F:6B:5E:E0:8A:7C:7D:94:60:96:28:55:CF:75 SHA1: D2:54:0E:97:86:53:D7:F5:E9:68:BC:C6:BF:42:62:88:38:15:BE:F4 Trust this certificate? [no]: yes Certificate was added to keystore
Configure iSQL*Plus to run in SSL mode.
Copy http-web-site.xml to secure-web-site.xml
cd $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/isqlplus/config cp http-web-site.xml secure-web-site.xml
Edit secure-web-site.xml and set the port number, and add the attribute secure="true":
<web-site port="4443" secure="true" display-name="Oracle9iAS Containers for J2EE HTTP Web Site">
The port you use for iSQL*Plus in SSL mode can be any free port on your machine. In this example, it is set to port 4443. The default SSL port is 443.
Add a new element to the web-site element in the secure-web-site.xml file.
<ssl-config keystore="/oracle/ora10g/oc4j/j2ee/keystore" keystore-password="123456" />
Edit server.xml to refer to the secure-web-site.xml file:
<web-site default="true" path="./secure-web-site.xml" />
For detailed information about implementing SSL, see the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Security Guide.
The Oracle Net connection between the iSQL*Plus Server and Oracle Database provides the same security as in previous client server architectures. For more information about Oracle Net connection security, see the Oracle Net Services Administrator's Guide and the Oracle Advanced Security Administrator's Guide.
You can edit the Application Server configuration file to disable iSQL*Plus.
To disable iSQL*Plus
Stop the Application Server.
Open server.xml located in $ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/isqplus/config.
Find the application tag for iSQL*Plus. It has the form <application name="isqlplus" ...>, and wrap with the comment tags, <!-- and -->. The syntax of the line to change in the configuration file to disable or enable iSQL*Plus is:
<application name="isqlplus" path="../applications/isqlplus.ear" auto-start="true" />
or to enable or disable iSQL*Plus Help, the application tag has the form, <application name="isqlplushelp" ...>. The syntax of the line to change in the configuration file to disable or enable iSQL*Plus Help is:
<application name="isqlplushelp" path="../applications/isqlplushelp.ear" auto-start="true" />
Start the Application Server.
The iSQLPlusAllowUserMarkup configuration option controls whether an iSQL*Plus Application Server enables users to use custom HTML in scripts.
You can edit the configuration file, web.xml, to set iSQLPlusAllowUserMarkup ON or OFF. The web.xml file is located in the directory:
$ORACLE_HOME/oc4j/j2ee/oc4j_applications/applications/isqlplus/isqlplus/WEB-INF
In the web.xml file, search for the <param-name> iSQLPlusAllowUserMarkup. The syntax of the line to change in the configuration file is:
<init-param> <param-name>iSQLPlusAllowUserMarkup</param-name> <param-value>none</param-value> <description>Valid values are: none | all</description> </init-param>
Where the parameter is set OFF, or if it does not exist or has an invalid value, users cannot use SET MARKUP HTML HEAD text BODY text TABLE text ENTMAP or COLUMN ENTMAP to create user defined HTML. If Map Special Characters to HTML Entities is set OFF in the Script Formatting Preferences screen, the value is ignored and reverts to ON. The default value for iSQLPlusAllowUserMarkup is OFF. Leaving it set OFF provides greater security.
Where the parameter is set ON, users can execute SET MARKUP HTML HEAD text BODY text TABLE text ENTMAP and COLUMN ENTMAP commands to change the status of entity mapping for the iSQL*Plus session or report column. This enables custom HTML to be included in iSQL*Plus report output.
Your web browser needs to be configured to enable cookies and JavaScript.
Your iSQL*Plus interface and online help default to the language of the operating system. However, data you retrieve and enter is determined by the language and territory parameters set by the NLS_LANG environment variable. See Chapter 12, "SQL*Plus Globalization Support" for more information.
Each iSQL*Plus login is uniquely identified, so you can:
Connect multiple times from the same machine
Connect multiple times from different machines
iSQL*Plus supports this stateful behavior by storing session context information in the Application Server. You must ensure that your Application Server always routes HTTP requests to the same server, otherwise the session context will not be found. However, you may find it useful to start more than one Application Server to distribute user load across the multiple servers.
Certain settings from a session are either retained or automatically filled in the next time you log in to iSQL*Plus from the same workstation:
Script Input area size
Number of History entries
Your username, password and Output preferences are not saved by iSQL*Plus. Your login details may be retained by your web browser.
Configuring the Windows Graphical User Interface is discussed in the following topics:
Choose Environment from the Options menu to display the Environment dialog which you can use to create a SQL environment statement for the current session.
Choose an item from the Set Options list to begin. You can use the default settings, or you can customize the settings by using the other dialog controls. The available controls vary with the options you choose. You can make multiple changes to options and values. When the text box is available, you can enter appropriate text or appropriate numeric values. Click OK to commit your settings.
|
Note: Options introduced in SQL*Plus Release 8.1 can only be accessed through the command-line and are not available in the SQL*Plus for Windows Environment dialog. These options are:SET APPINFO SET LOBOFFSET SET MARKUP SET SHIFTINOUT SET SQLBLANKLINES SET SQLPLUSCOMPATIBILITY {ON|OFF} See "Command Reference" in the SQL*Plus User's Guide and Reference for descriptions of these SET commands. |
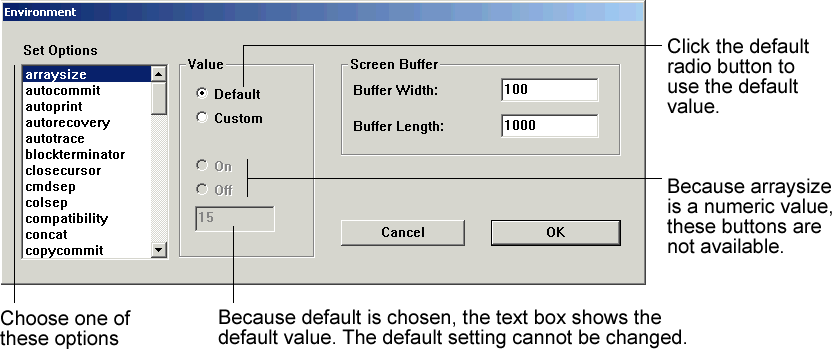
Example 3-2
The ARRAYSIZE is set to 15, the default value.
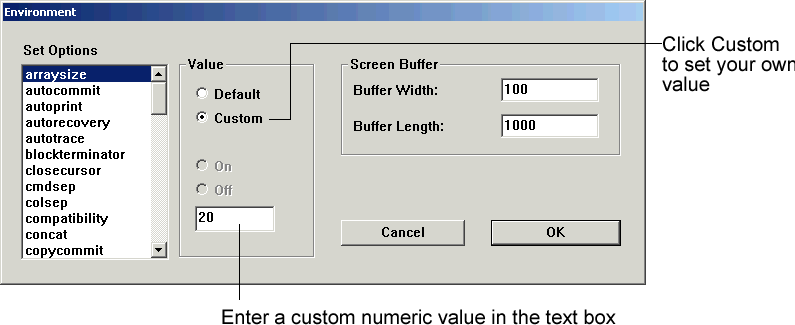
Example 3-3
To change the ARRAYSIZE, click Custom and enter the number in the text box.
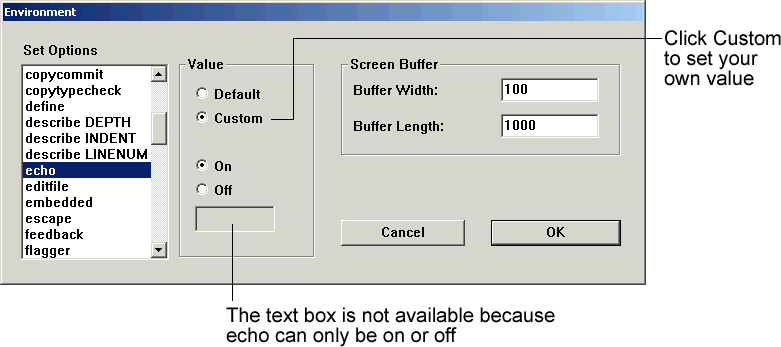
Example 3-4
The default for ECHO is off. To change the setting, click Custom and then click On.
This section describes how to customize your Windows GUI and command-line interface configuration by setting Windows registry entries.
|
Warning: Microsoft does not recommend modifying the registry. Editing the registry may affect your operating system and software installation. Only advanced users should edit the registry. Oracle takes no responsibility for problems arising from editing the Windows registry. |
When you install Oracle products for Windows, Oracle Universal Installer adds relevant parameters to the Windows registry.
The following table indicates which registry version(s), REGEDT32.EXE or REGEDIT.EXE, you can use for your particular Windows platform:
| Windows Platform | REGEDT32.EXE | REGEDIT.EXE |
|---|---|---|
| Windows XP Pro | YES | YES |
| Windows 2000 | YES | YES |
The HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE subkey contains the Oracle Database parameters.
See the Registry Editor's help system for instructions on how to edit the registry entries defining Oracle Database parameters.
If you change the value of an Oracle Database related registry entry or add a registry entry, you should restart SQL*Plus to ensure the changes take effect.
The SQLPATH registry entry specifies the location of SQL scripts. SQL*Plus searches for SQL scripts in the current directory and then in the directories specified by the SQLPATH registry entry.
The HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\HOME0 registry subkey (or the HOMEn directory for the associated ORACLE_HOME) contains the SQLPATH registry entry. SQLPATH is created with a default value of %ORACLE_HOME%\DBS. You can specify any directories on any drive as valid values for SQLPATH.
When setting the SQLPATH registry entry, you can concatenate directories with a semicolon (;). For example:
C:\ORACLE\ORA10\DATABASE;C:\ORACLE\ORA10\DBS
See the Registry Editor's help system for instructions on how to edit the SQLPATH registry entry.
The SQLPLUS_FONT registry entry defines the font face used in the SQL*Plus Windows GUI. It is located in the registry subkey, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\HOME0. If the SQLPLUS_FONT entry is not created, or if it has an invalid name or value, the default face, Fixedsys, is used.
See "To Change the Windows GUI Font and Font Size" for details on how to create the SQLPLUS_FONT registry entry and set the font face. See the Registry Editor's help system for instructions on how to edit the SQLPLUS_FONT registry entry.
The SQLPLUS_FONT_SIZE registry entry defines the font size used in the SQL*Plus Windows GUI. It is located in the registry subkey, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\HOME0. If the SQLPLUS_FONT_SIZE entry is not created, or if it has an invalid name or value, the default size, 16, is used.
See "Changing the Windows GUI Font and Font Size" for details on how to create the SQLPLUS_FONT_SIZE registry entry and set the font size. See the Registry Editor's help system for instructions on how to edit the SQLPLUS_FONT_SIZE registry entry.