| Oracle® Ultra Search User's Guide 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10731-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Ultra Search User's Guide 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10731-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
The ability to control user access to Web content is critical. This chapter describes the architecture and configuration of security for Ultra Search.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Configuring Ultra Search Security
|
See Also:
|
This section describes the Ultra Search security model. It contains the following sections:
Ultra Search Admin Privilege Model in the Hosted Environment
How Ultra Search Leverages the Identity Management Infrastructure
Security problems, such as unauthorized access to information, can lead to loss of productivity. Search engines like Ultra Search provide access to a vast variety of content repositories in a single gateway. Each one of these repositories has its own security model that determines whether a particular end user can access a particular document. Because Ultra Search provides access to data from multiple repositories, existing security information in each repository must be carefully supported to avoid unauthorized access.
This section describes the security architecture of Ultra Search. Security is implemented at the following levels:
User authentication
This is the identification of a user, through LDAP and Oracle Internet Directory, at Ultra Search front-end interfaces.
User entitlement
This determines whether a user can access information about a particular item in the results list. It is implemented by access control lists (ACLs). Ultra Search provides mapped-security to third-party repositories by retrieving the access control list for each document at the time of indexing and storing them in Ultra Search. Ultra Search does not need any connection with the repository itself to validate access privileges.
Security of Ultra Search
Actual Ultra Search security is handled by the dictionary data in the Ultra Search database, the administrative user, and password data.
Starting with Oracle Application Server 10g and Oracle Database 10g, Ultra Search supports secure socket layer (SSL), a worldwide standard for encryption over the HTTP protocol (HTTPS). In other words, all content crawling, indexing, and querying is encrypted using SSL. Ultra Search supports the crawling of Web sites with HTTPS. Also, in the Ultra Search administration tool, you can register HTML Forms, which are accessible with HTTPS.
|
See Also: "Configuring Ultra Search for SSL" for detailed information on configuring Ultra Search with SSL |
To grant an Ultra Search user administration privileges, you must assign the user to an administration group. Each user can belong to one or more groups. The following groups are created for each Ultra Search instance:
Instance administrators: Users in this group can only manage instances for which they have privileges.
Super-users: Users in this group can manage all instances, including creating instances, dropping instances, and granting privileges.
Ultra Search also has two classes of users:
Single Sign-on (SSO) users: These users are managed by the Oracle Internet Directory and are authenticated by the SSO server. The Ultra Search administration tool identifies all Ultra Search instances to which the SSO user has access. This is available only if you have the Oracle Identity Management infrastructure installed.
Database users (non-SSO): These users exist in the database on which Ultra Search runs.
New Ultra Search instances contain the following users:
WK_TEST: This is the instance administrator user that hosts the default instance, called WK_INST. In other words, WK_TEST is the instance administrator for WK_INST. For security purposes, WK_TEST is locked after the installation. The administrator should login to the database as DBA role, unlock the WK_TEST user account, and set the password to be WK_TEST. (The password expires after the installation.) If the password is changed to anything other than WK_TEST, then you must also update the cached schema password using the administration tool Edit Instance page after you change the password in the database.
WKSYS: This is a database super-user. WKSYS can grant super-user privileges to other users, such as WK_TEST. All Ultra Search database objects are installed in the WKSYS schema.
|
Note: TheWKUSER role is required to host instances. |
In a hosted environment, one enterprise (for example, an application service provider) makes Ultra Search available to other enterprises and stores information for them. The enterprise performing the hosting is called the default subscriber, and the enterprises that are hosted are called subscribers.
|
Note: This is available with the Oracle Application Server release and the Oracle Collaboration Suite release. This is not available with the Oracle Database release. |
The default subscriber and its search base are specified in the following attributes of the Oracle Internet Directory entry "cn=Common,cn=Products,cn=OracleContext":
orclDefaultSubscriber
orclSubscriberSearchBase
In a non-hosted environment, in which there are no subscribers, the enterprise installing Ultra Search is the default subscriber. All Ultra Search administration groups (super-user and instance administrator groups) are created under Default Subscriber Oracle Context (for example, cn=OracleContext,dc=us, dc=oracle, dc=com) in the Oracle Internet Directory Information Tree (DIT).
Figure 5-1 shows an example of the Oracle Internet Directory topology of a hosted environment. There are two subscribers (A and B) and the default subscriber. Each subscriber has its own super-user privilege group associated with it. There are four Ultra Search instances created in the Ultra Search back-end 'install 1'. 'Instance 1' is associated with the default subscriber. 'Instance 2' and 'Instance 3' are associated with 'Subscriber A'. 'Instance 4' is associated with 'Subscriber B'. Each Ultra Search instance has its instance administration group associated with it.
Figure 5-1 Oracle Internet Directory Topology of a Hosted Environment
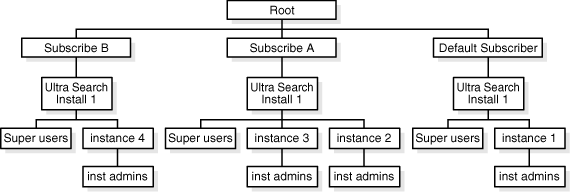
This section describes the privilege model of Ultra Search administration tool in the hosted environment. The model applies to both the SSO login mode an d the non-SSO login mode.
In non-SSO mode, only database users can login to the admin tool.
If the login database user has the super-user privilege, then the user can administer all Ultra Search instances across the default subscriber and any other subscribers.
If the login database user only has the admin privilege on a particular Ultra Search instance, then the user can administer the instance regardless of whether the instance is associated with the default subscriber or any other subscribers.
In SSO mode, only SSO users can login to the admin tool
If the SSO user belongs to the default subscriber, then the following is true:
If the SSO user has the super-user privilege, then the user can administer all Ultra Search instances across the default subscriber and any other subscribers (for example, instances 1,2,3,4).
If the SSO user has the admin privilege on a particular Ultra Search instance (for example, instance1) within the default subscriber, then the user can administer the instance (instance 1) that is associated with the default subscriber.
If the SSO user belongs to a subscriber, then the following is true:
If the SSO user has the super-user privilege, then the user can administer only Ultra Search instances within the subscriber to which he belongs. (For example, if the user from subscriber A has the super-user privilege, then the user can only administer instance 2 and 3.)
If the SSO user has the admin privilege on a particular Ultra Search instance (for example, instance 2), then the user can administer the instance (instance 2) that is associated with the subscriber (subscriber A).
To create or drop an Ultra Search instance, the user (either the database or the SSO user) must have the super-user privilege.
In non-SSO mode, the database user can create or drop an instance and associate the instance with any subscriber, including the default subscriber.
In SSO mode:
If the login SSO user belongs to the default subscriber, then the user can create or drop an instance and associate the instance with any subscriber, including the default subscriber.
If the login SSO user belongs to a particular subscriber, then when the user creates an instance, the instance is created and associated with the subscriber to which the login user belongs. Because the user might not have access to create the instance schema in the database, the user must inform the hosting company (default subscriber) to create the database schema for hosting the instance.
To grant or revoke a super-user, login to the administration tool as a super-user.
In non-SSO mode (database user login), only super-users can grant or revoke the super-user privilege to and from other database users.
In SSO mode:
If the login SSO user belongs to the default subscriber, then the user can do the following:
Grant or revoke the super-user privilege to SSO users in the default subscriber.
Grant or revoke the super-user privilege to SSO users in a particular subscriber.
If the login SSO user belongs to a particular subscriber, then the user can grant or revoke the super-user privilege to users within the same subscriber to which the login user belongs.
To grant or revoke an instance administrator, login to the admin tool as a super-user or an instance administrator.
In non-SSO mode (database user login), only super-users or instance administrators can grant or revoke the instance admin privilege to and from other database users.
In SSO mode:
The login SSO user can grant or revoke only the instance admin privilege to SSO users within the subscriber the instance as associated with. For example, the user can grant the admin privilege on 'Instance 2' or 'Instance 3' to an SSO user in subscriber A.
The login SSO user cannot grant or revoke the instance admin privilege to SSO users within a different subscriber. For example, the user cannot grant the admin privilege on 'Instance 2' or 'Instance3' to an SSO user in subscriber B.
All publicly crawled data is publicly accessible.
The following resources are protected by Ultra Search:
Access control list (ACL)-aware crawled data is protected; in other words, it is private to users named by the ACL.
All passwords are protected.
User-defined data source parameters are protected.
There are three possible entry points to Ultra Search:
The database: This contains all data. All data and metadata is protected with row level security. All passwords are encrypted.
The Ultra Search administration tool: This does not contain crawled data. You must authenticate with SSO or database authentication.
The Ultra Search query tool: This contains crawled data. Unauthenticated users can see only public data. Authenticated users can see public data and ACL-protected information. Users must authenticate themselves to see private information.
Ultra Search uses the following to leverage security services:
Ultra Search uses secure socket layers (SSL), the industry standard protocol for managing the security of message transmission on the Internet. This is used for securing RMI connections, HTTPS crawling, and secure JDBC.
JAZN: Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE (OC4J) implements a Java authentication and authorization service (JAAS) provider called JAZN. This provides application developers with user authentication, authorization, and delegation services to integrate into their application environments.
Ultra Search uses the SSO server and Oracle Internet Directory to leverage the Oracle Identity Management infrastructure.
With the SSO server, you can log on once for all components, and the Ultra Search administrative interface allows user management operations on either database users or SSO users. Authenticated SSO users never see the Ultra Search logon screen. Instead, they can immediately choose an instance. The Ultra Search administration tool and the query tool use SSO.
Oracle Internet Directory is Oracle's native LDAP v3-compliant directory service, built as an application on top of the Oracle database. Oracle Internet Directory hosts the Oracle common identity. All Ultra Search instances are registered with Oracle Internet Directory.
Ultra Search has native identity management; therefore, in the absence of the identity management infrastructure, Ultra Search uses native user management available with the Oracle database.
This section describes special security configuration steps within Ultra Search.
Storing clear text passwords in data-sources.xml poses a security risk. Avoid this by using password indirection to specify the password. This lets you enter the password in jazn-data.xml, which is automatically encrypted, and point to it from data-sources.xml.
Ultra Search has no specific security passwords.
|
See Also: "Configuring Security Framework Options for Ultra Search" for more information on Ultra Search configuration issues to leverage security |