| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Concepts 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B12016-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Concepts 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B12016-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Oracle Enterprise Manager (hereafter referred to as Enterprise Manager) is the Oracle integrated management solution for managing the complete Oracle environment. All services within your enterprise, including hosts, databases, listeners, application servers, HTTP Servers, and Web applications, are easily managed as one cohesive unit.
This chapter acknowledges the challenges you face as a database administrator and states how Enterprise Manager can help you meet these challenges.
This chapter describes:
The IT systems of today are growing more complex with each iteration of new technology. It is not unheard of to have 2,600 instances to manage. These instances can be as close as next door or on the other side of the world. By using Enterprise Manager, you can:
Extract the information needed for critical and timely decisions.
Manage the extraordinary number of systems in an efficient manner.
In conjunction with virus protection software, prevent viruses and worms from attacking your system.
Manage your ecosystem, that is, your Oracle platform and all your third-party software, including your storage systems, hosts, routers, and so on.
Reduce your hardware and labor costs, that is, manage thousands of systems as if they were one.
Mission-critical decisions are dependent on accessible and up-to-date information. The reporting mechanisms within Enterprise Manager can answer the following:
Why is it taking so long for banking transactions to process from the branch in London to the branch in New York? The answer is available using the Application Performance Management functionality.
We are forecasting our budget for next year. Do we foresee needing additional storage devices? If so, what machine needs these devices? Set up the Automatic Storage Management option to help analyze your needs.
Host XYZ is always going down. Why? Look at the home page for the host and analyze the information. Maybe the host needs to be reconfigured?
These are just a few of the questions enterprise Manager can help you answer. The up-to-the-minute information on the Grid Control provides clear and concise information.
Not only is this information available from any supported Web browser on any desktop, it is also available using any personal digital assistant (PDA) that supports Microsoft Pocket PC IE. The EM2Go mobile component of Enterprise Manager makes this instant availability of information possible without any additional work on your part.
With system components numbering into the thousands, it is unrealistic to think that you can manage these components individually. The solution is to combine components together and have them follow one set of rules. You can combine these components in a number of ways:
Create heterogeneous groups, database groups, and host groups.
In Enterprise Manager, a group is a collection of targets. (Targets are components that you monitor or configure using Enterprise Manager.) You can define a database-specific group, a host-specific group, or define a heterogeneous group for a specific purpose.
A group can include any of the following: Oracle Management Agents, Application Servers, Beacons, Databases, database groups, HTTP servers, hosts, OIC LDAP Servers, Oracle Management Service and Oracle Management Repository, Web Applications, as well as other components.
For example, you can define a group to:
Reflect a particular function within your company, for example, manufacturing
Represent a geographic location, for example, European countries
Serve as a division of labor, for example, all the targets assigned to a particular administrator
Organize targets by type, for example, Management Agents
Combine targets that are on the same maintenance schedule, for example, for blackouts and backups
Create Oracle Application Server farms.
Oracle Application Server instances can be grouped and managed together by adding standalone instances to a single Oracle Application Server Metadata Repository. The collection of instances within a single metadata repository is known as an Oracle Application Server farm.
Having an Oracle Application Server farm is helpful because it is the first step in creating an Oracle Application Server cluster. Another benefit of a farm is having access to a single page with which to view and access all instances that use a common metadata repository.
Create Oracle Application Server clusters.
A cluster is a collection of Application Server instances with identical configuration and application deployment. Clusters enforce homogeneity among member instances so that a cluster of Application Server instances can appear and function as a single instance. Changes you make to one instance of a cluster are propagated to all members of the cluster. Clusters work only with J2EE and Web Cache middle tiers.
Unfortunately, we hear of computer systems being attacked by worms, viruses, and hackers. These attacks can cost millions of dollars in damage to files and systems, lost productivity, and if the attacks are to a Web site, millions of dollars in lost revenue.
Enterprise Manager, together with virus protection software, provides the security you need to prevent these hideous invasions by:
Notifying you of critical patch advisories
When a patch needs to be applied to prevent security problems, you are notified of such patches on the Grid Control home page. Enterprise Manager examines your enterprise configuration to determine whether the appropriate patches have been applied.
Providing notice of policy violations
You can use Enterprise Manager to see whether Oracle databases and hosts in your enterprise configuration are following database and host policies. On the host and the database home pages, you are notified of such policy violations. The policies identify security vulnerabilities, such as missing patches, open ports, access vulnerabilities, and so on.
Notifying you of critical patch advisories and policy violations is only a small part of how Enterprise Manager protects you and your systems from undesirable behavior.
In most production environments, you install and distribute the components of Enterprise Manager on multiple computers throughout your enterprise. For example, you might install your Management Repository on one system, install the Management Service on another system, and install Management Agents on each of the host computers you want to manage.
|
See Also: "Providing a Flexible Architecture" for information about the components of the Enterprise Manager Framework |
The security features of Enterprise Manager are packaged as a set of capabilities called Enterprise Manager Framework Security. Enterprise Manager Framework Security provides safe and secure communication channels between the components of Enterprise Manager. For example, it provides secure connections between your Management Service and its Management Agents.
Enterprise Manager Framework Security is designed to secure your Enterprise Manager installation and prevent:
Tampering or unauthorized review of credentials and sensitive management data while the data is in transit
Accidental or malicious installations of Management Agents that can upload data to your Management Service and Management Repository
Malicious calls to the Management Service or Management Agents from an external source
Unauthorized processes masquerading as a Management Service in order to collect data from Management Agent uploads
Enterprise Manager Framework Security implements these security features with industry-standard security tools and procedures that have been implemented and proven effective for other Oracle software products.
In particular, Enterprise Manager Framework Security takes advantage of:
HTTPS and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) components, including signed digital certificates and public keys, for communications between the Management Service and the Management Agents
|
See Also: "The Public Key Infrastructure Approach to Security" in Oracle Security Overview for an overview of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) features |
Oracle Advanced Security for communications between the Management Service and the Management Repository
Detailed instructions for enabling Enterprise Manager Framework Security are available in Oracle Enterprise Manager Advanced Configuration.
Today's corporations are looking at every possible way to save money. They need to do more with less and need to be competitive and conscious of costs. The bottom line is to save money!
By using Enterprise Manager, you can add targets and administrative accounts without scalability concerns. The underlying framework of Enterprise Manager can easily adapt to these additions. When you add a new target to Enterprise manager, all you need to do is to add a Management Agent to the target's host.
When you need to grow the enterprise even more, for example to other countries, add Oracle Management Services as needed.
Consolidation is driven by reducing management costs. The more you can run your individual systems as a cohesive unit, the less you will need to spend for labor.
Enterprise Manager provides the tools and framework needed for you to manage all the pieces that comprise your system and hardware environment. This section provides information about the following:
In Enterprise Manager, the Oracle Ecosystem is the organization of software and hardware and its environment functioning as a unit. The Grid Control Home page provides a unified view of your ecosystem. It gives one view of everything and the interdependencies of related targets.
Figure 1-1 Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control Home Page
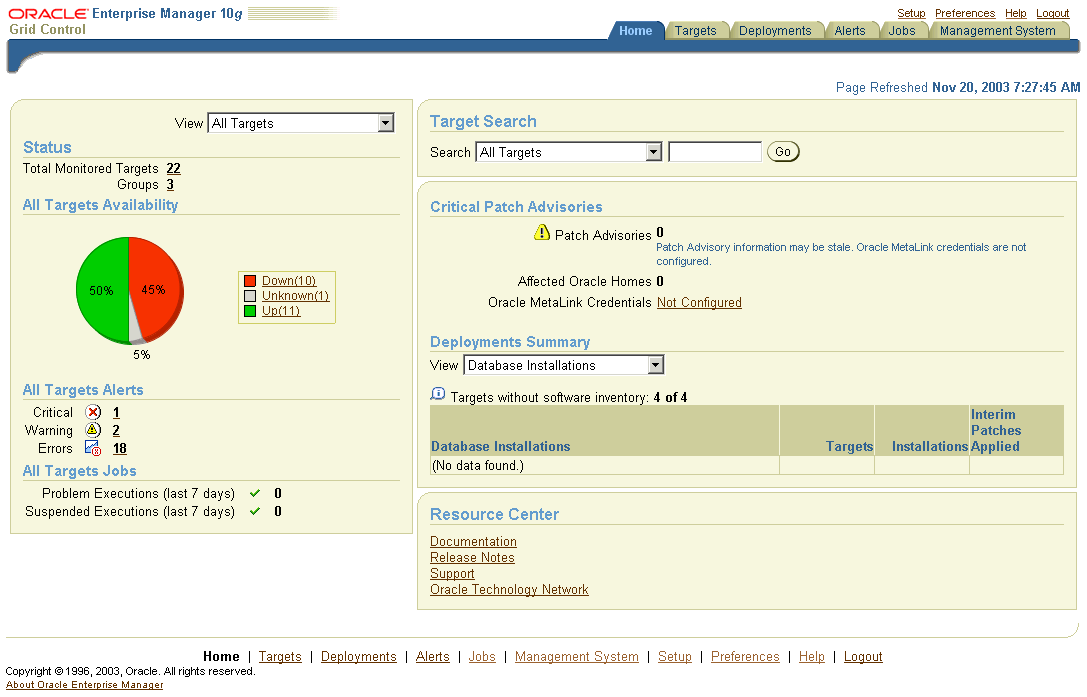
The Oracle Ecosystem manages, but is not limited to managing, the following components:
Database
Oracle Application Server
Oracle Collaboration Suite
Hosts (for example, Solaris, Linux, Windows)
Groups (applications and grids)
The following are examples of using Enterprise Manager to manage your ecosystem.
Using Oracle Database Management, you can:
Study top performance problems by analyzing the Top SQL pages. These pages assess the problem SQL statements and provide recommendations for correcting the problems.
Check the health of a target of a database group by analyzing the Database Group Maintenance page. For example, in the Configuration Advice sections of this page, you may see the rule that the control file for your database is not adequate. The message states:
Use at least two control files, multiplex them on different disks.
By connecting to MetaLink, determine whether there are any patches that need to be applied to your database. This information is available in the Hardware and Software Configuration section of the Database Group Maintenance page.
Monitor cluster databases on the Database Home page. In addition to the typical database information, this page also lists the cluster to which this database belongs.
Using Oracle Application Server, you can:
Identify the components of the Application Server and their current status, and drill down to obtain more details on the performance of the components.
Monitor real-time performance of the Application Server from the Performance property page.
View the top applications performance problems and drill-downs by accessing the Application Server's J2EE applications page.
By connecting to MetaLink, determine whether there are any patches that need to be applied to your Application Server. This information is available by clicking Patch in the Related Links section of the Application Server Home page. From the Patch: Select Patch page, you can then search for missing patches.
Using Host and Host Configuration, you can:
Analyze the top processes by CPU and memory on the Host Performance page.
Keep track of your hardware and software inventory using the Host Configuration page. By clicking Operating System Details, you can view the operating system properties. By clicking Hardware Details, you can analyze the hardware associated with this host.
Study the top performance problems by analyzing the Performance page related to a host.
Grid computing encompasses the pooling and provisioning of resources, and workload management. There are many components and systems tied together that make grid computing possible.
The Web-based Grid Control (Figure 1-1) exposes information and management functionality using HTTP, so you can perform your management tasks using a standard browser such as Netscape or Internet Explorer. The framework provides a standard Grid Control login URL through which an administrator gains access to Enterprise Manager. The management content of the Grid Control is organized to allow different classes of users to see customized views of management information that are appropriate for their needs.
The key to grid computing is managing separate entities as a whole. Enterprise Manager provides this manageability through the definition and use of groups, database clusters, hosts, and application server clusters. This greatly simplifies the complexity of your grid and reduces the time needed to manage these entities.
You can define groups with the purpose of comparing metrics of similar targets. This enables you to define the thresholds for the metrics of a particular group only once and then copy these thresholds to other groups. This comparison is particularly useful when dealing with host and database groups.
Database clusters are optional structures for storing table data. Clusters are groups of one or more tables physically stored together because they share common columns and are often used together. Because related rows are physically stored together, disk access time improves. When you define database clusters, you can then manage these structures as a single unit.
An Application Server cluster is a collections of application server instances with identical configuration and application deployment. Clusters enforce homogeneity between member instances so that a cluster of Application Server instances can appear and function as a single instance. With appropriate front-end load balancing, any instance in an Application Server cluster can serve client requests. This simplifies configuration and deployment across multiple instances and enables fault tolerance among clustered instances.
Defining a grid can be an ongoing process. You can start small and add as you go. For example, by defining groups, database clusters, and Application Server clusters, you have the beginnings of a grid. You can then manage these entities as single units.
Though grouping information is important, it is only a small portion of Grid Computing. The efficiency of resource utilization sharing and dedicating resources are crucial to the success of Grid Computing:
The architecture of the Enterprise Manager framework provides a high level of flexibility and functionality. You can easily customize Enterprise Manager to suit the monitoring and administrative needs of your environment.
Enterprise Manager is a lightweight multi-tiered framework that enables you to centrally manage your applications over the Intranet and Internet using a Web-based Grid Control. Access to Enterprise Manager management services and applications use standard Internet technology. Hence, you can easily adapt Enterprise Manager to work seamlessly through corporate firewalls for remote management.
You can also extend the framework, by using the Software Developer's Kit, to include new target types that are unique to your environment. For example, you can quickly define new target types to allow users to collect monitoring information from managed targets specific to their enterprise environment. The typical Enterprise Manager framework configuration consists of these functional areas (Figure 1-2):
Responsible for monitoring all targets on the host, for communicating that information to the middle-tier Management Service, and for managing and maintaining the host and its targets.
Oracle Management Agents monitor and perform administrative functions on managed targets in your enterprise. Targets include but are not limited to Databases, Application Servers, Listeners, and Third-party Applications.
A J2EE Web application that renders the user interface for the Grid Control, works with all Management Agents in processing monitoring and job information, and uses the Management Repository as its data store.
Two tablespaces in an Oracle database that contain information about administrators, targets, and applications that are managed within Enterprise Manager.
The Management Service uploads to the Management Repository the monitoring data it receives from the Management Agents. The Management Repository then organizes the data so that the data can be retrieved by the Management Service and displayed on the Grid Control.
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Grid Control
Enterprise Manager Web-based user interface for centrally managing your entire computing environment. The Grid Control is installed from a separate CD–ROM that is part of the Oracle Database 10g Release 1 (10.1) CD–ROM Pack.
From the Grid Control, you can monitor and administer your entire computing environment from one location on the network. All the services within your enterprise, including hosts, databases, listeners, application servers, HTTP Servers, and Web applications, are easily managed as one cohesive unit.
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Grid Control Framework
The Grid Control relies on various underlying technologies to discover, monitor, and administer your computing environment.
The Grid Control Framework consists of the Grid Control and these underlying technologies:
One or more Oracle Management Services
The Oracle Management Repository
Remote Oracle Management Agents, installed on each monitored host.
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Database Control
The Enterprise Manager Web-based application for managing Oracle Database 10g Release 1 (10.1). The Database Control is installed and available with every Oracle Database 10g installation.
From the Database Control, you can monitor and administer a single Oracle Database instance or a clustered database.
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Database Control Framework
The Database Control relies on various underlying technologies to discover, monitor, and administer the Oracle Database environment.
The Database Control Framework consists of the Database Control and its underlying technologies:
A local version of the Oracle Management Service designed to work with the local database or clustered database
A local Oracle Management Repository installed in the local database and designed to store management data for the Database Control
A local version of the Oracle Management Agent designed to provide monitoring data to the local Management Service
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control
The Enterprise Manager Web-based application for managing Oracle Application Server 10g (9.0.4). The Application Server Control is installed and available with every Application Server 10g installation.
From the Application Server Control, you can monitor and administer a single Oracle Application Server instance, a farm of Oracle Application Server instances, or Oracle Application Server Clusters.
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control Framework
The Application Server Control relies on various underlying technologies to discover, monitor, and administer the Oracle Application Server environment.
The Application Server Control Framework consists of the Application Server Control and its underlying technologies:
Oracle Dynamic Monitoring Service (DMS)
Oracle Process Management Notification (OPMN)
Distributed Configuration Management (DCM)
A local version of the Oracle Management Agent specifically designed to gather monitoring data for the Application Server Control.
|
See Also: The Application Server Documentation Library for more information about the Application Server technologies |
Targets are the entities that Enterprise Manager manages. Examples of targets include but are not limited to: hosts, databases, application servers, and listeners. As your environment changes, you can add and remove targets from Enterprise Manager as needed. Many of the commonly used managed targets have been defined as part of the base Enterprise Manager product. They are automatically pre-configured for management when a management-ready product is installed. Oracle applications, Oracle databases and applications servers, and many of the operating systems that run Oracle products, are management-ready. Even though a target is predefined for instance monitoring levels, thresholds, and notification rules, you can still customize Enterprise Manager to your liking. That is, you can still perform value-added instrumentation to access more of the rich management functionality of Enterprise Manager than is provided with the standard target configuration.
The Oracle Management Agent identifies your targets, collects the data about those targets, and detects problems in your environment, for example, high CPU usage. A typical management framework deployment has one Management Agent on each host that is part of the enterprise. The Management Agent is responsible for the managed targets that are running on that host.
To store and process the information collected by the Management Agent, and to instruct the Management Agent to perform administrative tasks, the Management Agent relies on that part of Enterprise Manager that provides the core functionality of the framework – the Oracle Management Service.
The Management Service tier (J2EE Web applications) can be divided into several major components. These include:
Management servlets that perform management and administrative functions
Management Repository where information collected by the Management Agents from managed targets is consolidated
Management administration and maintenance services
User interface technology to organize and present management information content to any Web browser
The management service tier can be further distributed in high-end environments for performance. For example, you can install the Management Repository on a separate host from the one running the Management Service. The framework can also be collapsed into the managed target tier to support a standalone deployment configuration (Management Repository, Management Service, and Management Agent reside on a single host).
Management information is stored in a Management Repository. The Management Repository consists of schema definitions, RDBMS jobs, and stored procedures running inside an Oracle database. The information in the Management Repository includes:
Configuration details about the managed targets
Historical metric data and alert information
Client and Web server response time information
Managed target availability information
Product and patch inventory information
The richness of information stored in the Management Repository is useful for tasks such as end-to-end reporting, problem diagnosis, as well as service-level agreement and availability reporting. Information stored in the repository, can be shared between any number of administrators accessing Central Consoles that point to the central Management Repository.