This chapter describes how to use Enterprise Security Manager to administer Enterprise User Security in Oracle Databases. This chapter contains the following topics:
Enterprise User Security Administration Tools Overview
Enterprise Security Manager and Enterprise Security Manager Console are the two main tools provided for administering Enterprise User Security.
Use Enterprise Security Manager to create and manage
- Enterprise domains
- Enterprise roles
Use Enterprise Security Manager Console to create, manage, and configure
- Enterprise users
- Enterprise User Security administrative groups
- Identity management realm properties.
These tools are introduced in Chapter 2, "Configuration and Administration Tools Overview" where you can find information about starting each tool and navigating its interface.
In particular, refer to the following topics to get started using Enterprise User Security administration tools:
Administering Identity Management Realms
An identity management realm is a subtree of directory entries, all of which are governed by the same administrative policies. A realm Oracle Context is a subtree in a directory identity management realm that contains the data used by any installed Oracle product that uses the directory. Enterprise Security Manager is one such product. It lets you manage database and security-related information in an identity management realm.
This section describes how to use Enterprise Security Manager to administer directory identity management realm properties that pertain to Enterprise User Security. It contains the following topics:
Identity Management Realm Versions
Enterprise User Security can only use an identity management realm supplied by Oracle Internet Directory 10g (9.0.4) or later, which ships with Oracle Application Server 10g (9.0.4). You can manage Enterprise User Security directory entries in a version 9.0.4 identity management realm by using Enterprise Security Manager for Oracle Database 10g.
Enterprise Security Manager displays all existing version 9.0.4 identity management realms in its main application tree.
Note:
Enterprise User Security did not require identity management realms in Oracle8i, nor in Oracle9i. In those previous releases, only an Oracle Context was used. For Oracle Database 10g Enterprise User Security, full identity management realms and their associated realm Oracle Contexts must be used.
|
Setting Properties of an Identity Management Realm
An identity management realm has a number of properties that can be viewed and managed by using Enterprise Security Manager. These properties are described in Table 13-1.
Table 13-1 Identity Management Realm Properties
Setting Login Name, Kerberos Principal Name, User Search Base, and Group Search Base Identity Management Realm Attributes
Setting these identity management realm attributes enables the database to locate Enterprise User Security entries.
To set Login Name, Kerberos Principal Name, User Search Base, and Group Search Base identity management realm attributes:
- Navigate to the Enterprise Security Manager Console home page. (Choose Launch Enterprise Security Manager Console from the Operations menu and log in by using your OracleAS Single Sign-On username and password.)
- Choose the Realm Configuration tab.
- In the Realm Information window, enter the appropriate information into the available fields.
- Click Submit to save your changes to the directory.
Setting the Default Database-to-Directory Authentication Type for an Identity Management Realm
Setting the default database-to-directory authentication type, enters a value for the LDAP_DIRECTORY_ACCESS initialization parameter. This parameter is set on individual databases when they are registered in Oracle Internet Directory.
To set the default database-to-directory authentication type for an identity management realm:
- Select the identity management realm in the left navigator pane.
- Choose the General tab in the right main window.
- In the Realm Attribute Settings region of the General tabbed window, choose either PASSWORD or SSL from the Database to Directory list.
- Click Apply to save your changes to the directory.
Managing Identity Management Realm Administrators
An identity management realm contains administrative groups that have varying levels of privileges. The administrative groups for an identity management realm, which pertain to Enterprise User Security, are defined in Table 13-2. For more information about these groups, see "Administrative Groups".
Table 13-2 Enterprise User Security Identity Management Realm Administrators
To manage identity management realm administrators:
- Navigate to the Enterprise Security Manager Console home page. (Choose Launch Enterprise Security Manager Console from the Operations menu and log in by using your OracleAS Single Sign-On username and password.)
- Choose the Users and Groups tab.
- In the Users and Groups tabbed window, choose the Group subtab.
- In the Group subtab window, select the administrative group you wish to edit, and click Edit.
- In the Edit Group window, enter group information into the appropriate fields. You can change group owners, add users to or remove them from groups, and view group membership.
- Click Submit to save your changes to the directory.
Administering Enterprise Users
Enterprise Security Manager manages one directory server at a time, identified at the top of the main application tree. It lets you manage enterprise users and data that is relevant to Enterprise User Security in the identity management.
This section describes how to use Enterprise Security Manager to administer enterprise users. It contains the following topics:
Creating New Enterprise Users
Use Enterprise Security Manager to create users in the directory.
To create new enterprise users:
- Select Launch Enterprise Security Manager Console from the Operations menu. The Enterprise Security Manager Console home page appears (Figure 13-1). Log in with your OracleAS Single Sign-On username and password.
Figure 13-1 Enterprise Security Manager Console Home Page
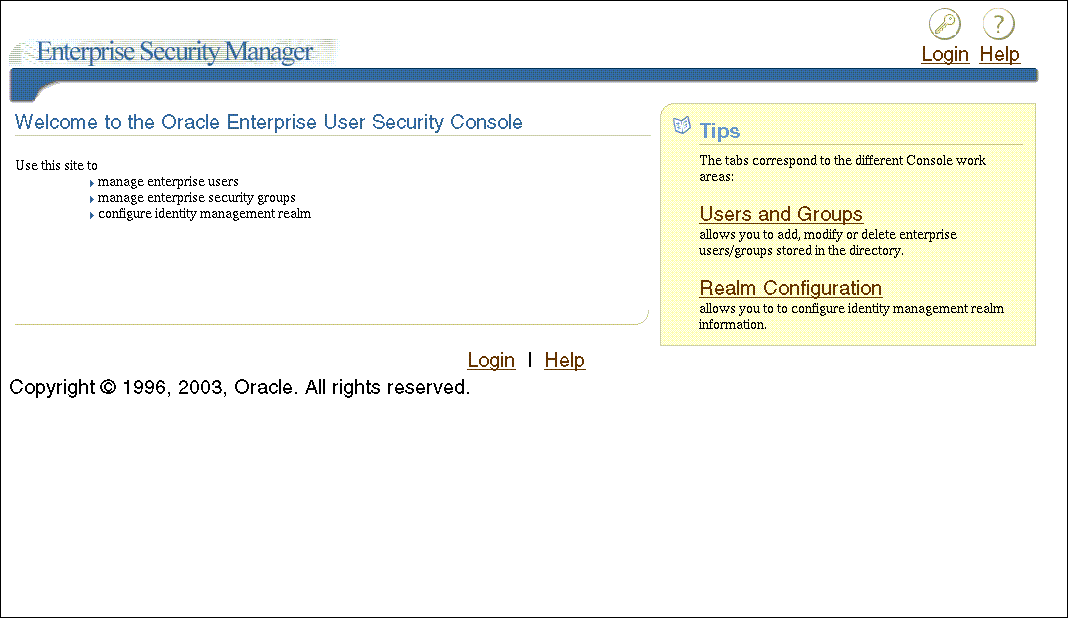
Text description of the illustration esmconso.gif
- Choose the Users and Groups tab.
- In the Users and Groups tabbed window, choose the User subtab, if it is not already displayed.
- In the User subtab window, click Create (located on the upper right corner of the Search Results table). Note that if your users are authenticated to the database by using Kerberos credentials, and the krbPrincipalName attribute is not there, then see "Configuring Enterprise Security Manager Console for Kerberos-Authenticated Enterprise Users" for information about how to configure this.
- Enter the appropriate user information in the Create User window and click Submit to create a new enterprise user.
Setting Enterprise User Passwords
You can set and maintain enterprise user passwords in the Basic Information region of the Enterprise Security Manager Console Edit User window (Figure 13-2).
Figure 13-2 Enterprise Security Manager Console Edit User Window: Basic Information
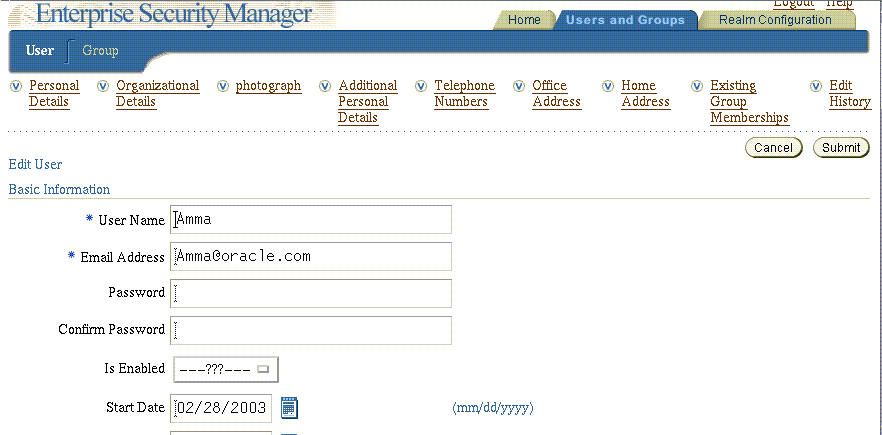
Text description of the illustration edituser.gif
The enterprise user password is used for:
- Directory logon
- Database logon, to databases that support password authentication for global users
To set the password for an enterprise user:
- Navigate to the Enterprise Security Manager Console home page. (Choose Launch Enterprise Security Manager Console from the Operations menu and log in using your OracleAS Single Sign-On username and password.)
- Choose the Users and Groups tab.
- In the Users and Groups tabbed window, choose the User subtab, if it is not already displayed.
- In the User subtab window, enter part of the enterprise user's username (login name) or e-mail address, and click Go.
A list of all users that match your search criteria displays.
- Select the user for whom you wish to create a new password, and click Edit.
- In the Edit User window, enter the new password, and click Submit.
Defining an Initial Enterprise Role Assignment
When you create a new enterprise user, you can grant any previously configured enterprise roles to the new user.
To assign existing enterprise roles to a new enterprise user:
- In the left navigator pane, choose the Users icon under the Users, By Search Base folder, which display under the identity management realm you are using. The list of users displays in the right main window.
- Select a user in the main window, and click Edit.... An Edit User window displays.
- Choose the Enterprise Roles tab of the Edit User window, and click Add....
The Add Enterprise Roles window appears (Figure 13-3):
Figure 13-3 Enterprise Security Manager: Add Enterprise Roles Window
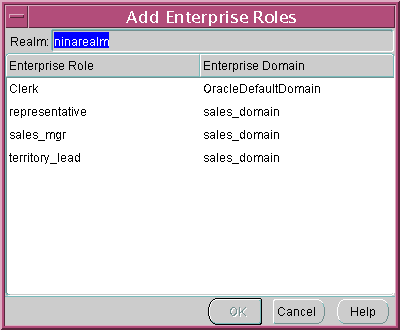
Text description of the illustration esm0009.gif
- Select the correct identity management realm, then select any enterprise roles in your realm to assign to the new user, and choose OK.
Browsing Users in the Directory
Enterprise Security Manager lets you browse the directory for all users currently stored there in two ways--by using Enterprise Security Manager Console, or by using the All Users tab in the main application window.
To browse enterprise users in the directory by using Enterprise Security Manager Console:
- Navigate to the Enterprise Security Manager Console home page. (Choose Launch Enterprise Security Manager Console from the Operations menu and log in by using your OracleAS Single Sign-On username and password.)
- Choose the Users and Groups tab.
- In the Users and Groups tabbed window, choose the User subtab, if it is not already displayed.
- In the User subtab window, enter part of the enterprise user's username (login name) or e-mail address, and click Go. To display all users, do not enter search criteria.
A list of all users that match your search criteria displays. You can browse through the displayed users and select one to Edit, Delete, or Assign Privileges. If you need to create a new user, click Create.
To browse enterprise users in the directory by using the All Users tab in the main application window:
- Select the directory in the left navigator pane.
- Choose the All Users tab in the right main window (Figure 13-4):
Figure 13-4 Enterprise Security Manager: Main Window (All Users Tab)
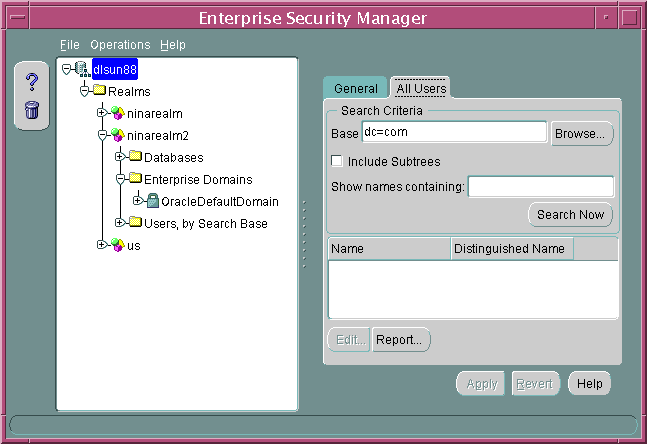
Text description of the illustration esm0011.gif
- Define the search criteria and click Search Now. The window displays the results of the search. Table 13-3 summarizes the search criteria and their respective effects on the search results.
Table 13-3 Directory Search Criteria
Note that you can also browse enterprise users in the directory by selecting realm_name > User, by Search Base > Users in the left navigation pane of the main application window.
Administering Enterprise Domains
An identity management realm contains an enterprise domain called OracleDefaultDomain. The OracleDefaultDomain is part of the realm when it is first created in the directory. When a new database is registered into a realm, it automatically becomes a member of the OracleDefaultDomain in that realm. You can create and remove your own enterprise domains but you must not remove the OracleDefaultDomain from a realm.
This section describes how to use Enterprise Security Manager to administer enterprise domains in the directory. It contains the following topics:
Creating a New Enterprise Domain
If you do not want to use the OracleDefaultDomain, then you can create a new enterprise domain in your identity management realm.
To create a new enterprise domain in an identity management realm:
- Start by using one of the following methods:
- Select Create Enterprise Domain from the Operations menu.
- Select a realm from the main application tree with a right mouse-click.
The Create Enterprise Domain window appears (Figure 13-5):
Figure 13-5 Enterprise Security Manager: Create Enterprise Domain Window
Text description of the illustration esm0023.gif
- In the Create Enterprise Domain window, select the appropriate Realm from the list (Figure 13-5).
Note:
If you invoked the Create Enterprise Domain window by right-clicking the realm in the main application tree, the name of that realm is already selected.
|
- Enter the name of the new enterprise domain, in the Domain Name field.
- Choose OK. The new enterprise domain is created in the realm, and appears on the main application tree.
To remove an enterprise domain:
- Select the target enterprise domain from the main application tree.
- Use either of the following methods:
- Select Remove Enterprise Domain from the Operations menu.
- Select an enterprise domain from the main application tree with a right mouse-click.
- Enterprise Security Manager asks you to confirm removal of the enterprise domain from the realm. Choose OK to remove it.
Note:
You cannot remove an enterprise domain from an identity management realm if that enterprise domain contains any enterprise roles.
|
Defining Database Membership of an Enterprise Domain
Use the navigation tree of the main Enterprise Security Manager window to select a specific enterprise domain. You can then use the Databases tab to manage database membership of an enterprise domain in a realm (Figure 13-6):
Figure 13-6 Enterprise Security Manager: Databases Tab (Database Membership)
Text description of the illustration esm0025.gif
To remove a database from an enterprise domain:
- Select a specific database for removal, and choose Remove.... The database is removed from the list.
- Choose Apply. The database is removed from the enterprise domain.
To add a database to an enterprise domain:
Note:
The following restrictions apply to adding databases to an enterprise domain:
- A database must be in an enterprise domain for enterprise users to be able to connect to it.
- You can only add a database to an enterprise domain if both the database and the enterprise domain exist in the same realm.
- A database cannot be added as a member of two different enterprise domains.
|
- Choose Add.... The Add Databases window appears. This window lists all the databases associated with the realm (Figure 13-7):
Figure 13-7 Enterprise Security Manager: Add Databases Window
Text description of the illustration esm0026.gif
- Select a new database to be added to the enterprise domain.
- Choose OK. The selected database is added to the list of databases in the Databases tabbed window (Figure 13-6).
- Choose Apply (Figure 13-6). The new database is added to the enterprise domain.
Managing Database Security Options for an Enterprise Domain
Use the Databases tabbed window (Figure 13-6) to manage database security options applicable to all databases that are members of the enterprise domain.
Database security options are summarized by Table 13-4:
Table 13-4 Enterprise Security Manager Database Security Options
Managing Enterprise Domain Administrators
An Enterprise Domain Administrator is a directory user with privileges to modify the content of that domain. You can use the Administrators tabbed window to manage Enterprise Domain Administrators when an enterprise domain is selected under an realm in the main application tree.
To add a new user to the list of Enterprise Domain Administrators:
- In the left navigator pane, select the enterprise domain to which you wish to add administrators.
- In the right pane, select the Administrators tab.
- Choose Add.... The Add Users window appears. Use this window to locate and select users for designation as Enterprise Domain Administrators. The new users appear in the Administrators tabbed window.
- Choose Apply. The new Administrators are added to the enterprise domain.
To remove a user from the list of Enterprise Domain Administrators:
- In the left navigator pane, select the enterprise domain from which you wish to remove administrators.
- In the right pane, select the Administrators tab.
- Select a user from the list of Administrators.
- Choose Remove. The selected user is removed from the list.
- Choose Apply. The user is removed as an Enterprise Domain Administrator for that domain in the realm.
Managing Enterprise Domain Database Schema Mappings
Database schema mappings, also referred to as user schema mappings) let databases that are registered in the directory accept connections from users without requiring any dedicated database schemas for them. For example, when local user Scott connects to a database, a database schema called Scott must exist--for that logon to be successful. This can be difficult to maintain if there are thousands of users and perhaps hundreds of databases in a very large enterprise.
Users that are defined in an LDAP-compliant directory do not require dedicated schemas on every Oracle9i or later database to which they might connect.
A database can use a schema mapping to share one database schema between multiple directory users. The schema mapping is a pair of values: the base in the directory at which users exist, and the name of the database schema they will use.
You can use the Database Schema Mappings tabbed window to manage database schema mappings--when a database is selected under a realm in the main application tree or when a domain is selected. If a domain is selected, these mappings apply to all databases that are members of the enterprise domain. Therefore, each database in the enterprise domain must have a schema of the same name used in the mapping for that mapping to be effective on that database. This window contains a list of database schema names, directory DNs, and mapping types (Figure 13-8):
Figure 13-8 Enterprise Security Manager: Database Schema Mappings Tab
Text description of the illustration esm0020.gif
To add a new mapping to the list of database schema mappings in the enterprise domain:
- In the Database Schema Mapping tabbed window, choose Add....
The Add Database Schema Mappings window appears (Figure 13-9). Use this window to locate and select a base in the directory and pair it with a database schema name, to make a database schema mapping. There are three components to the window: there is a directory search tree from which to select the user's DN or the base of users, the option to choose either subtree-level or entry-level mapping, and a field in which to enter a schema name.
Figure 13-9 Enterprise Security Manager: Add Database Schema Mappings Window
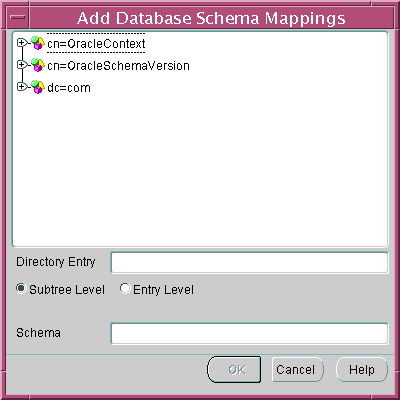
Text description of the illustration esm0021.gif
- Navigate the directory to select a desired entry as a base for the database schema mapping. This can be any directory entry but should be either the actual user (entry-level) or located above the subtree of users to be mapped (subtree-level). You can also edit the contents of the Directory Entry field in this window to manually define the base.
- Choose the mapping type: Subtree Level or Entry Level. Note that subtree-level mapping is usually the most useful.
- Enter the name of the database schema for which this Mapping will be made into the Schema field, and choose OK. This must be a valid name, for a schema that already exists on that database.The new database schema mapping appears in the database schema mappings window (Figure 13-8).
- Choose Apply. The new database schema mapping is added to the selected database or domain in the realm.
To remove a mapping from the list of database schema mappings in an enterprise domain:
- Select a mapping by selecting from the Database Schema Mapping tabbed window.
- Choose Remove. The selected Mapping is removed from the list.
- Choose Apply. The mapping is removed from the enterprise domain.
Managing Password Accessible Domains
There are three requirements for a database to accept a connection from a password-authenticated user:
- The database must be a member of a domain configured to accept Password authentication (See: Table 13-4).
- The domain must be a member of a password-accessible domains group, called the Password-Accessible Domains List, added by a member of either the OracleContextAdmins or the OracleDBSecurityAdmins directory administrator groups. Domain members (databases) of this list can read the user's password verifier in the directory, while those excluded from this list cannot.
- The user entry must be in a directory subtree of users that has been enabled for Oracle database access.
To configure password accessibility:
- Select the enterprise domain in the left navigator pane.
- Choose the Databases tabbed window and select Password or All Types from the User Authentication methods listed. (See Figure 13-6)
- Click Apply.
To add a domain to the Password-Accessible Domains List:
- Select the identity management realm in the left navigator pane.
- Choose the Accessible Domains tabbed window and click Add. The Add Accessible Enterprise Domains dialog box appears. See Figure 13-10.
Figure 13-10 Enterprise Security Manager: Add Accessible Enterprise Domains Dialog Box
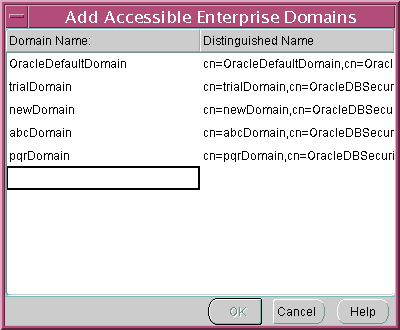
Text description of the illustration esmpwacc.gif
- Select the OracleDefaultDomain from the list of enterprise domains, and click OK. The OracleDefaultDomain is added to the password-accessible domains list.
Note:
- By default, the
cn=Users subtree in an identity management realm has ACLs (access control lists) to enable appropriate database access to user password attributes. If you do not use this subtree to store users, then see Oracle Internet Directory Administrator's Guide for information about setting up proper ACLs for another user search base.
- The OracleDefaultDomain is a member of the password-accessible domains list by default, but it can be removed.
|
To remove an enterprise domain from the password-accessible domains list:
- Select the identity management realm in the left navigator pane.
- Choose the Accessible Domains tabbed window and select the enterprise domain that you want to remove from the list.
- Click Remove.
Managing Database Administrators
A Database Administrator is a directory user that has privileges to modify the database and its subtree in the realm. Database Administrators may be managed by using the Administrators tabbed window when a database is selected under a realm in the main application tree.
To remove a user from the list of Database Administrators:
- In the Administrators tabbed window, select a user from the list of administrators.
- Choose Remove; the selected user is removed from the list.
- Choose Apply; the user is removed as a Database Administrator for that database.
To add a new user to the list of Database Administrators:
- In the Administrators tabbed window, choose Add; the Add Users window appears. Use this window to locate and select users in the directory.
- Select a user or users from the directory to be added as a Database Administrator; the new user(s) is displayed in the Administrators tabbed window.
- Choose Apply; the new Administrator(s) is added to the database in the realm.
Administering Enterprise Roles
An enterprise domain within an identity management realm can contain multiple enterprise roles. An enterprise role is a set of Oracle role-based authorizations across one or more databases in an enterprise domain.
This section describes how to use Enterprise Security Manager to administer enterprise roles in the directory. It contains the following topics:
Creating a New Enterprise Role
You can create an enterprise role in an enterprise domain either from the Operations menu on the Enterprise Security Manager main window (Figure 13-8), or by right-clicking an enterprise domain in the main application tree. In either case, the Create Enterprise Role window appears (Figure 13-11):
Figure 13-11 Enterprise Security Manager: Create Enterprise Role Window
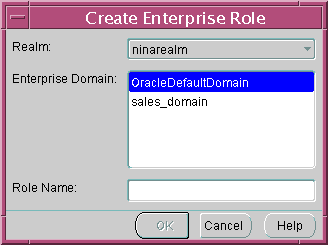
Text description of the illustration esm0030.gif
To create a new enterprise role:
- Choose the target identity management realm from the list. This is the realm containing the target enterprise domain to hold the new enterprise role.
Note:
If you invoked the Create Enterprise Role window by right-clicking an enterprise domain, the name of the identity management realm is already selected.
|
- Select the appropriate enterprise domain for the new enterprise role, from the Enterprise Domain list.
Note:
If you invoked the Create Enterprise Role window by right-clicking an enterprise domain, the name of the enterprise domain is already selected.
|
- Enter the name of the new enterprise role in the Role Name field.
- Choose OK. The new enterprise role is created in the enterprise domain, and appears on the main application tree.
To remove an enterprise role:
- Select the target enterprise role from the main application tree (Figure 13-8).
- Choose Remove Enterprise Role, either from the Operations menu or by right-clicking the enterprise domain in the main application tree.
- Enterprise Security Manager asks you to confirm the removal of the enterprise role. Choose Yes.
Assigning Database Global Role Membership to an Enterprise Role
Use the Database Global Roles tabbed window (Figure 13-12) of the Enterprise Security Manager main window to manage database global role membership in an enterprise role. This window lists the names of each global role that belongs to the enterprise role, along with the name of the database on which that global role exists.
Figure 13-12 Enterprise Security Manager: Database Global Roles Tab
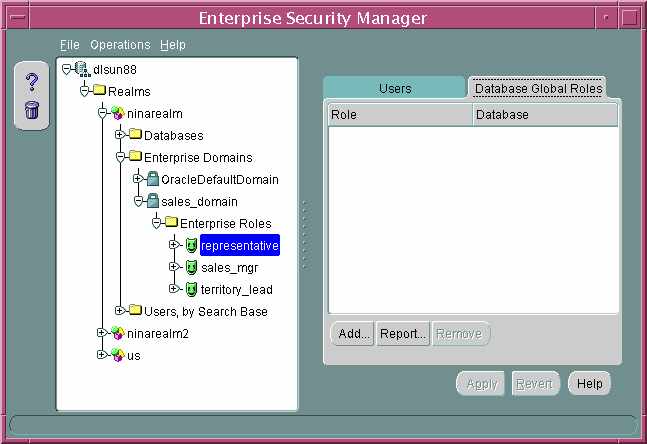
Text description of the illustration esm0031.gif
When populating an enterprise role with different database roles it is only possible to reference roles on databases that are configured to be global roles on those databases. A global role on a database is identical to a normal role, except that the Database Administrator has defined it to be authorized only through the directory. (Global roles are created with the syntax, CREATE ROLE <role_name> IDENTIFIED GLOBALLY ' ';) A Database Administrator cannot locally grant and revoke global roles to users of the database.
To add a global role to an enterprise role:
- Choose Add... (Figure 13-12). The Add Global Database Roles window appears. This window lists all of the databases in the enterprise domain--from which global roles can be selected to add to an enterprise role.
- Select a database from which to obtain global roles. A window appears and prompts you for logon details to authenticate to the database (and fetch global roles). Typically, this is a DBA logon to that database.
Note that the name of the database appears in the Service field by default. You can use this name to connect to the database if your Oracle home has LDAP enabled as its Oracle Net naming method, or if this name appears as a TNS alias in your local Oracle Net configuration. Otherwise, you can overwrite the content of the Service field with any other TNS alias configured for that database, or by a connect string in the format <host>:<port>:<oracle sid>. For example, cartman:1521:broncos.
Figure 13-13 Enterprise Security Manager: Database Authentication Required Window
Text description of the illustration esm0034.gif
- Choose OK. Enterprise Security Manager connects you to the given database and fetches the list of global roles supported on that database. The list of values, if any, is displayed in the Add Global Database Roles window.
- Select one or more global roles from the list of returned values and choose OK. These global roles appear in the Database Global Roles tabbed window (Figure 13-12).
- Choose Apply. The new global roles are added to the enterprise role in the enterprise domain.
To remove a database global role from an enterprise role:
- Select a global role from the list in the main application tree, and choose Remove.... The global role is removed from the list.
- Choose Apply. The global role is removed from the enterprise role in the enterprise domain.
Granting Enterprise Roles to Users
You can grant an enterprise role to users in two ways: you can select a user and add a role (see "Defining an Initial Enterprise Role Assignment"), or you can select a role and add a user. When you grant an enterprise role to a user, it includes all database global roles contained within that enterprise role. Use the Users tabbed window.
To grant an enterprise role to users:
- Select the role in the navigation tree, and choose Add... in the Users tabbed window. The Add Enterprise Users window appears. Use this window to locate and select one or more directory users to add as enterprise role grantees (Figure 13-14):
Figure 13-14 Enterprise Security Manager: Add Enterprise Users Window
Text description of the illustration esmadusr.gif
- Select a user or users and click OK. The new grantees are added to the list of users who have that enterprise role in the enterprise domain.
- Choose Apply. The user or users are granted the selected enterprise role.
To remove a user from the list of enterprise role grantees:
- Select a user from the list of grantees in the Users tabbed window.
- Choose Remove. The selected user is removed from the list.
- Choose Apply. The user is removed as a grantee for that enterprise role in the enterprise domain.













